NASA’s Curiosity rover has been exploring an area of Mars known as Gale Crater, because landing. It was tasked with analyzing the habitability of Mars. What exactly was Mars enjoy in the past? Were the conditions appropriate for life?
Allow ’so be clear, Curiosity wasn’t armed if circumstances weren’t right for life to have lived, but it can inform us.
During its time around the red planet, Curiosity has discovered a little enigma: Mars has methane and the abundance changes with the seasons. Substantial flashes of methane can imply that some type of procedure is occurring, but that’s not the situation. Plus it s not a indication of life.
Methane is a gas produced by one of two approaches on Earth: biological and geological. That means that some type of life form may be generating or even there’so some type of geological explanation.
This is puzzling to scientists back on Earth because the Martian methane has been detected by ground-based telescopes. But recent data from Mars shows the minuscule amounts of methane are all gone.
In fact, the Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO)–a joint European and Russian mission–that started in 2016 and has been developed to sniff-out trace gases, such as methane, states the Martian atmosphere is basically methane-free.
However, NASA’s Curiosity rover might have taken a large step ahead.
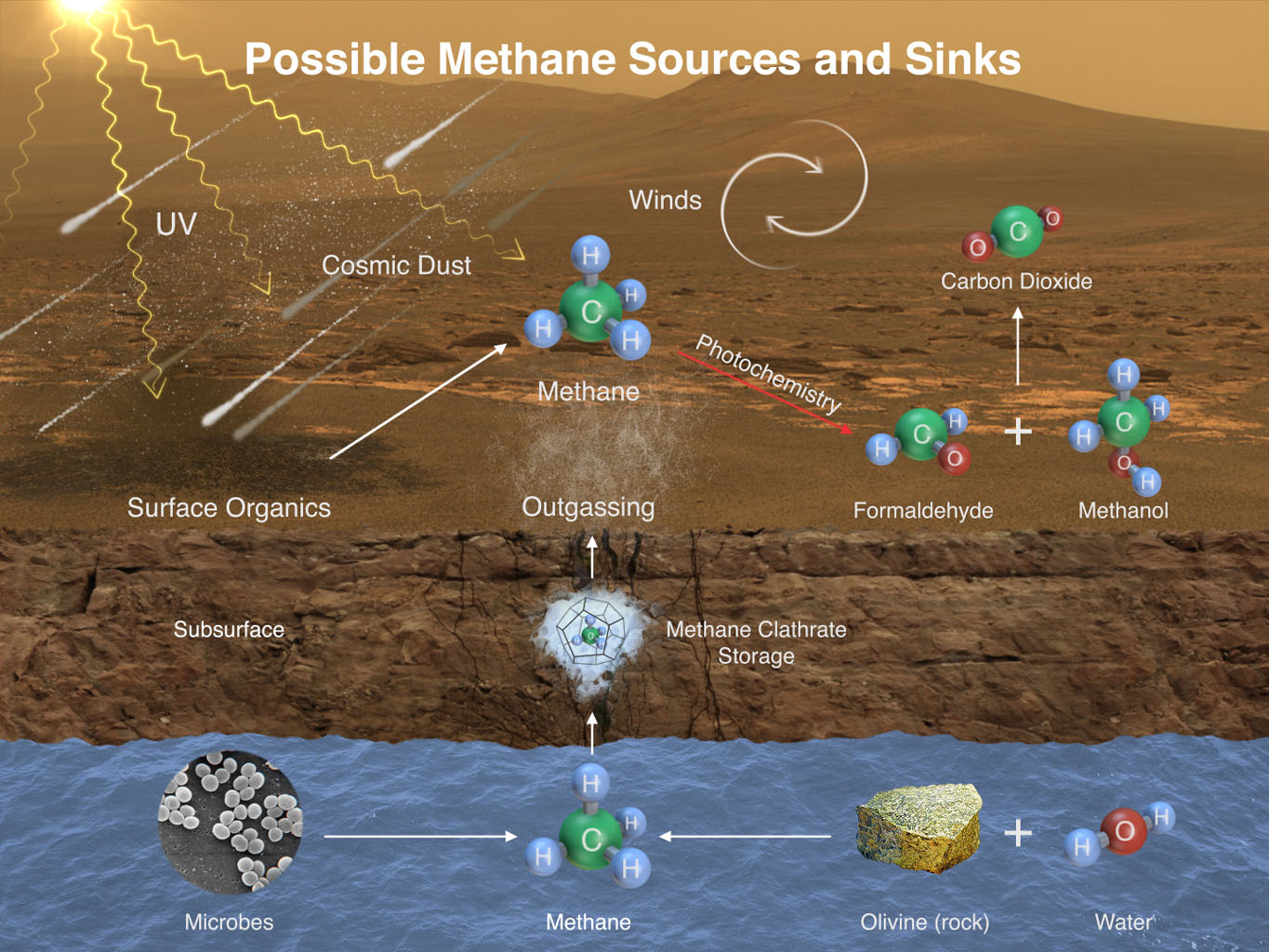 Possible sources and sinks of methane on Mars. Credit: NASA
Possible sources and sinks of methane on Mars. Credit: NASA
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
S detection of methane is not anything new. Even the six-wheeled rover has detected surges in methane. The most recent occurrence, recorded in June 2019, showed staggeringly significant levels of methane–21 ppb (parts per billion). That’s the greatest the rover has recorded thus far.
Neither TGO nor its counterpart, the Mars Express orbiter, detected any methane whatsoever in June.
TGO has detected minute amounts of methane–approximately 0.012 ppb–during its first couple of months of science operations. That’s equivalent to about 30 times less than what Curiosity sees. (Mars Express did find the very first methane surge that Curiosity seen in June 2013.)
Why is there a discrepancy between ground measurements and orbital data? The Curiosity science team has a couple of ideas.
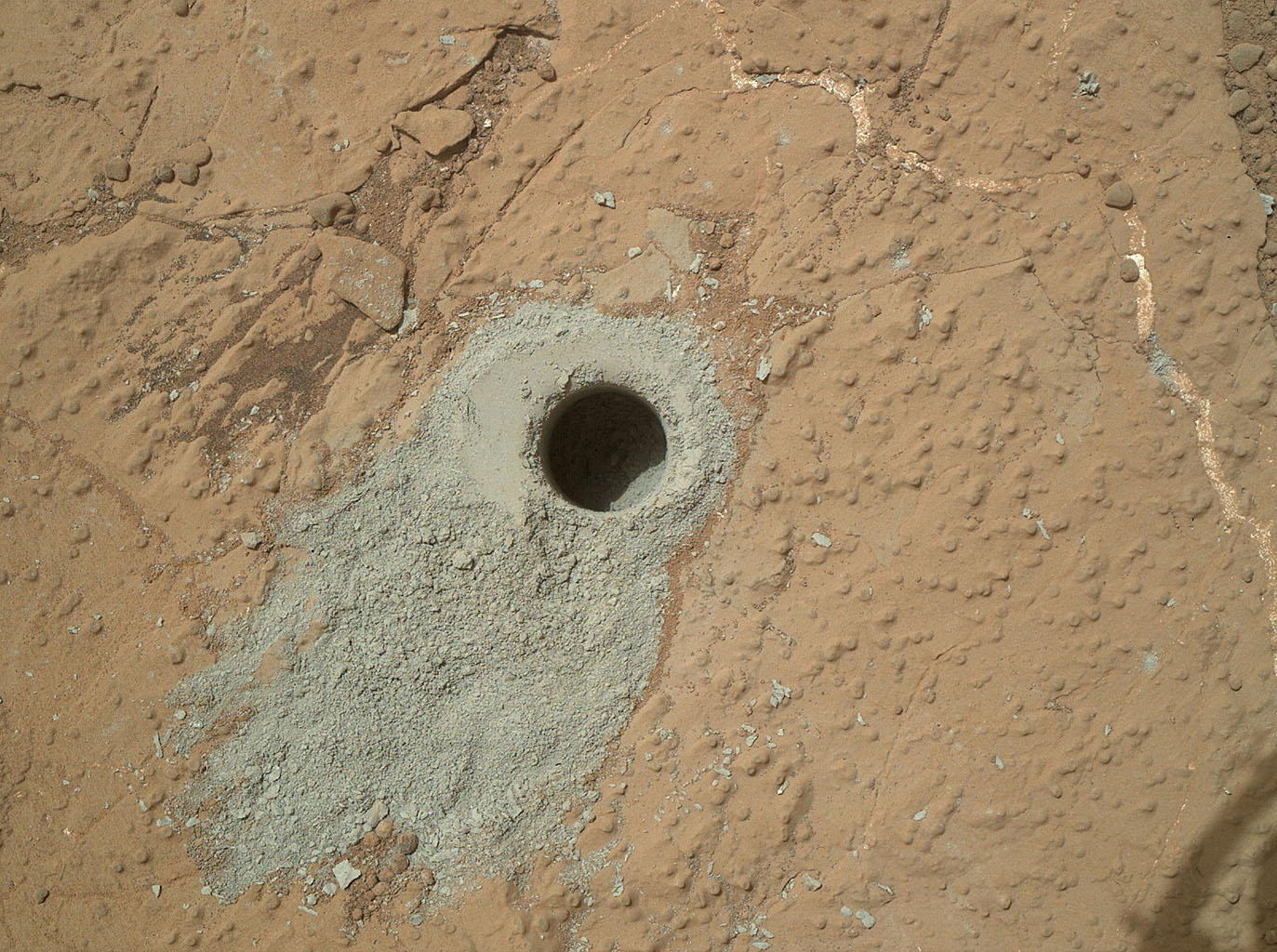 Curiosity drills to the ground to examine samples. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Curiosity drills to the ground to examine samples. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
First off, there may be some type of atmospheric procedure occurring that’s scrubbing it out. Curiosity takes dimensions on the ground and detects the methane, while TGO transforms the planet and doesn’t. This means that something happens to it as it travels upwards through the air.
Another explanation may be atmospheric expansion and contraction. Mars has an atmosphere, albeit a remarkably thin one compared to Earth’s. Every single evening the warmth from sunlight causes the air to expand and contract.
The methane could become more diffuse, Since the air expands throughout the daytime. Since Curiosity step methane at night, once the rover is busy, it could explain the methane appears more abundant. That means that the rover is currently sniffing the air when would be higher.
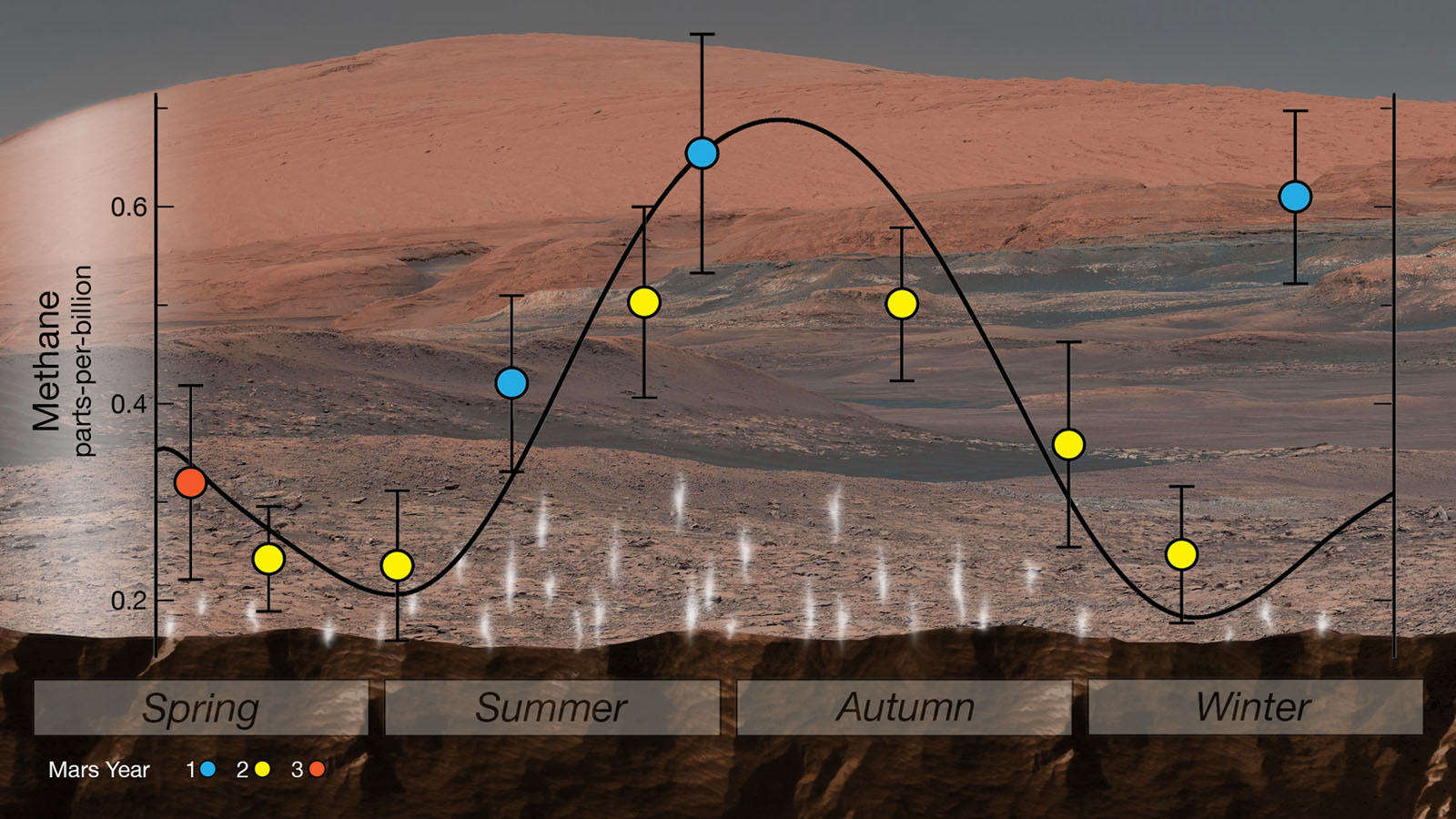 NASA’s Curiosity rover detects seasonal fluctuations in atmospheric methane in Gale Crater. The methane sign has been observed for nearly three Martian years (nearly six Earth years), peaking every summer. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA’s Curiosity rover detects seasonal fluctuations in atmospheric methane in Gale Crater. The methane sign has been observed for nearly three Martian years (nearly six Earth years), peaking every summer. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Compare these with data and the team plans to take a methane dimensions. This will give the team some insights to the data is indeed different. Once they have that puzzle solved, they can move onto bigger questions?
It s also completely possible that the gas might have been created billions of years back in , underground pockets that are underground, and it s today seeping up through the bedrock. More dimensions and Just time can inform.
NASA is sending its own next-generation Mars rover into the planet this July. Dubbed the Mars 2020 rover, the vehicle is now currently a souped-up model of Curiosity. This rover will not just have the ability to search for biosignatures (or even indications of lifetime ), it will even bag samples up for a potential return to Earth.
The article Mars rover on Earth, this red planet has a methane issue appeared initially on TESLARATI.
Article Source and Credit teslarati.com https://www.teslarati.com/mars-rover-detects-methane-problem/ Buy Tickets for every event – Sports, Concerts, Festivals and more buytickets.com

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.